Last updated on October 14, 2025
Hair growth isn’t a uniform or constant process. Each strand of hair grows at its own pace and follows a natural rhythm, moving through a cycle of growth, rest and renewal. This means that at any given time, some hairs are actively growing, while others are resting, shedding, or preparing to regrow. That’s why it’s perfectly normal to lose a few hairs each day without noticing a difference in overall volume.
Understanding the four main stages of hair growth can help you better interpret changes in your hair’s thickness, length, or shedding patterns. It also provides insight into common concerns like excessive shedding, patchy thinning, or a general slowdown in growth.
In this guide, we’ll walk through each phase of the cycle, which includes anagen, catagen, telogen and exogen, as well as explain how disruptions in the process can lead to hair loss. We’ll also explore treatment options available at Crown Clinic for those concerned about persistent hair fall or visible thinning.
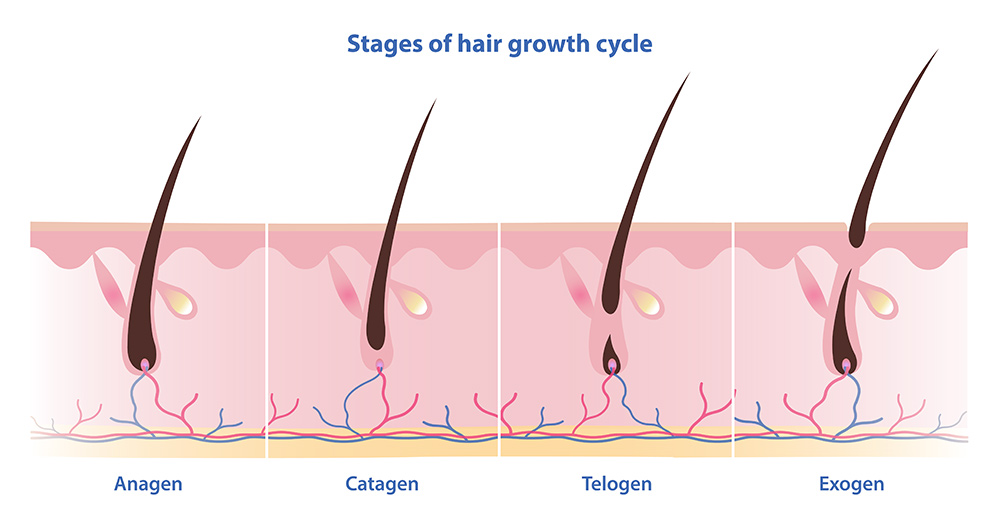
The four phases of the hair growth cycle consist of the anagen phase, the catagen phase, the telogen phase and the exogen phase.
The Four Key Phases of the Hair Growth Cycle
Each hair follicle on your scalp functions independently. This is why you never lose all your hair at once, as different follicles are in different phases at different times. Here’s a closer look at how the cycle works and what each stage involves:
1. Anagen Phase: The Growth Phase
The anagen phase is the most active part of the cycle. During this time, hair is growing continuously as cells in the follicle divide rapidly to produce new strands. This phase can last anywhere from two to seven years, depending on your genetics, overall health and hair care practices.
During the anagen phase, your hair grows at an average rate of one centimetre every 28 days. Most of the hair on your scalp, typically between 85 to 90 percent, is in this phase at any given moment.
The longer a strand stays in anagen, the longer it can grow, which is why people with healthier follicles or strong family genetics tend to grow longer hair. Maintaining a long and healthy anagen phase is key to achieving thick, strong and resilient hair.
2. Catagen Phase: The Transitional Phase
Once the growth period comes to an end, each hair enters the catagen phase. This is a short transitional stage that usually lasts for about two to three weeks. Hair growth slows down and eventually stops. During this time, the hair follicle shrinks and separates from the blood supply that previously sustained active growth.
Only about one to two percent of your hair is in the catagen phase at any one time. Although brief, this phase plays a crucial role by allowing the follicle to reset and prepare for the next cycle of growth. It is a natural pause that ensures hair can be renewed in a healthy, balanced way.
3. Telogen Phase: The Resting Phase
After the follicle transitions, it enters the telogen phase, where the hair remains in place but is no longer growing. This phase typically lasts for three to four months. While nothing appears to be happening on the surface, a new hair is quietly forming underneath the scalp, preparing to replace the old one.
At any given moment, around 10 to 15 percent of your hair is in the telogen, or resting, phase. This is completely normal and part of the hair’s natural cycle.
However, when a much larger number of hairs shift into this phase all at once, you may begin to notice sudden, diffuse shedding across the scalp. This condition is called telogen effluvium, and while it’s typically temporary, it can be quite alarming. It is often triggered by factors such as intense stress, major illness, hormonal changes, or significant life events like surgery or childbirth.
4. Exogen Phase: The Shedding Phase
The exogen phase is the final part of the cycle. This is when the old hair strand is released and falls out, allowing the new one growing beneath it to emerge. Shedding during this stage is completely normal, with most people losing between 50 to 100 hairs per day.
The exogen phase can last anywhere from two to five months. If you notice a sudden or excessive increase in daily hair loss, it could be a sign that this phase has been prolonged or that the next anagen cycle isn’t initiating properly. Such disruptions can affect your overall hair density over time.

When the hair growth cycle is disrupted, it can result in thinning, patchy hair loss or increased shedding.
What Happens When the Hair Growth Cycle Is Disrupted?
The hair growth cycle relies on a delicate balance between all four stages. When this balance is disrupted, the effects can become visible through thinning, patchy hair loss, or increased shedding. Common causes of disruption include:
- High levels of stress, which can push follicles prematurely into the telogen or exogen stages
- Hormonal changes related to pregnancy, menopause, thyroid issues, or birth control
- Nutritional deficiencies, particularly low iron or protein intake
- Scalp conditions or inflammation that impair follicle function
Identifying which stage of the cycle is affected helps guide treatment. For example, if fewer hairs are entering or staying in the anagen phase, your hair may struggle to grow long or thick. If too many hairs remain in telogen or exogen, shedding becomes more noticeable and prolonged.
Hair Loss Treatments at Crown Clinic
Whether you’ve noticed a shift in growth patterns, persistent thinning, or an increase in daily shedding, we’re here to help.
Our doctor-led, evidence-based treatments are designed to target the root of the problem and restore balance to the hair growth cycle. By addressing the health of the follicles and supporting new growth, we aim to deliver visible, lasting improvements tailored to your needs.
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)
This method involves transplanting individual follicles from a donor area into thinning or inactive regions of the scalp. It’s particularly effective for areas where hair has stopped cycling through the anagen phase.
Sapphire Hair Transplant
Using precision sapphire blades, this technique allows for more refined incisions and natural-looking results. It’s a preferred choice for patients seeking minimal scarring and faster recovery times.
Non-Surgical Treatments
If surgery isn’t right for you, Crown Clinic offers a variety of non-invasive therapies such as growth factor therapy, exosome treatment and medication treatment plans. These options are especially beneficial for stimulating follicles stuck in the resting or shedding phases and improving blood flow to promote healthy regrowth.
Every treatment plan begins with a personalised consultation so we can fully assess your hair loss concerns, evaluate your current hair cycle stage and recommend a strategy that aligns with your goals.
Book a Free Hair Consultation
Not sure if your hair is shedding more than usual? Wondering if what you’re experiencing is just a temporary phase or something that requires professional treatment?
At Crown Clinic, we bring over 50 years of experience in hair restoration and offer a truly personalised approach to treatment. Our expert team can help you understand which phase your hair is in, identify any disruptions and offer personalised options to encourage healthy regrowth.
Call us on +61 2 9134 4788 or book your free consultation here to get started.
FAQs
How do you know if your hair is in the resting phase?
Hair in the telogen phase remains in place but no longer grows. You may notice more shedding during washing or brushing, especially if many hairs have entered this phase at once.
How can you tell if your hair is in the anagen phase?
Hair in the anagen phase is actively growing. You’ll see a gradual increase in length, and the strands often appear thicker and more resilient. Clinic-based tools like trichograms can provide a closer look at how many hairs are currently growing.
How long does each stage of the cycle last?
- Anagen (growth): 2 to 7 years
- Catagen (transition): 2 to 3 weeks
- Telogen (rest): 3 to 4 months
- Exogen (shedding): 2 to 5 months
Duration can vary depending on your health, hormones and genetic profile.
What is the shortest stage of hair growth?
The catagen phase is the shortest, lasting only a few weeks. It is a necessary step to transition hair from active growth to rest.
At which stage does hair grow the fastest?
Hair growth is most active during the anagen phase. This is when the follicle receives the most nutrients and energy, leading to continuous lengthening of the strand.